基本概念
策略模式:是一种行为型设计模式。定义一系列算法族,将每个算法封装起来,并使它们可以相互替换。策略模式让算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的客户端。
核心思想:将算法的责任和使用算法的责任分开,封装成独立的策略类,使得算法可以在不影响调用方的情况下动态切换。
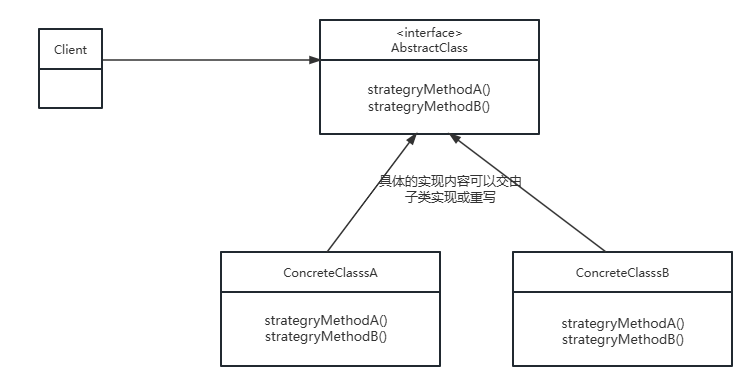
核心结构
- 策略接口(
Strategy):定义所有支持的算法的公共接口
- 具体策略(
ConcreteStrategy):实现策略接口,封装具体算法
- 上下文(
Context):持有策略接口的引用,负责调用策略算法
示例说明
场景:设计一个电商平台的促销系统,需要支持多种折扣计算策略(如固定金额折扣、百分比折扣、满减折扣),并且允许后续灵活添加新的折扣策略。
- 设计策略顶层接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public interface DiscountStrategy {
double calculate(double originalPrice);
String getDescription();
}
|
- 固定金额折扣策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class FixedAmountDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
private double discountAmount;
public FixedAmountDiscount(double discountAmount) {
this.discountAmount = discountAmount;
}
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return Math.max(0, originalPrice - discountAmount);
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "固定金额折扣:减" + discountAmount + "元";
}
}
|
- 百分比折扣策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public class PercentageDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
private double discountPercent;
public PercentageDiscount(double discountPercent) {
this.discountPercent = discountPercent;
}
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
return originalPrice * discountPercent;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "百分比折扣:" + (discountPercent * 10) + "折";
}
}
|
- 满减折扣策略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public class FullReduceDiscount implements DiscountStrategy {
private double fullAmount;
private double reduceAmount;
public FullReduceDiscount(double fullAmount, double reduceAmount) {
this.fullAmount = fullAmount;
this.reduceAmount = reduceAmount;
}
@Override
public double calculate(double originalPrice) {
if (originalPrice >= fullAmount) {
return originalPrice - reduceAmount;
}
return originalPrice;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "满" + fullAmount + "减" + reduceAmount + "元";
}
}
|
- 模式应用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public class Order {
private double originalPrice;
private DiscountStrategy discountStrategy;
public Order(double originalPrice) {
this.originalPrice = originalPrice;
}
public void setDiscountStrategy(DiscountStrategy discountStrategy) {
this.discountStrategy = discountStrategy;
}
public double calculateFinalPrice() {
if (discountStrategy == null) {
return originalPrice;
}
return discountStrategy.calculate(originalPrice);
}
public String getOrderDetails() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("原价: ¥").append(originalPrice).append("\n");
if (discountStrategy != null) {
sb.append("折扣策略: ").append(discountStrategy.getDescription()).append("\n");
}
sb.append("最终价格: ¥").append(calculateFinalPrice());
return sb.toString();
}
}
|
- 测试验证
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
public class StrategyPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Order order = new Order(200.0);
order.setDiscountStrategy(new FixedAmountDiscount(50.0));
System.out.println("策略1:" + order.getOrderDetails() + "\n");
order.setDiscountStrategy(new PercentageDiscount(0.8));
System.out.println("策略2:" + order.getOrderDetails() + "\n");
order.setDiscountStrategy(new FullReduceDiscount(199.0, 60.0));
System.out.println("策略3:" + order.getOrderDetails());
}
}
|
结果展示:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
执行结果
策略1:
原价: ¥200.0
折扣策略: 固定金额折扣:减50.0元
最终价格: ¥150.0
策略2:
原价: ¥200.0
折扣策略: 百分比折扣:8.0折
最终价格: ¥160.0
策略3:
原价: ¥200.0
折扣策略: 满199.0减60.0元
最终价格: ¥140.0
|
对于商品促销策略,这是变化的部分,针对这种情况有一个设计原则:识别应用中变化的方面,把它们和不变的方面进行分离,换句话说,如果每次有新的需求,某方面的代码就要变,那么这个行为应可以抽离出来,与不变的代码进行分离。
定义促销策略时,使用一个促销的接口定义不同促销策略共同的方法,这就涉及到第二个设计原则:
针对接口编程,而不是针对实现编程,将促销策略共同的方法抽象到接口中,具体的策略实现其策略逻辑,客户端调用不需要知道其内部实现。
将多个促销策略用不同的子类实现, order通过组合的形式进行调用,这就涉及到第三个设计原则:
优先使用组合而不是继承,使用组合时设计具备很大的弹性。不仅把一个算法家族封装进它们自己的一组类,而且可在运行时改变其行为,只要组合的对象实现正确的接口,这在许多设计模式中都可以看到。
其类图如下:
总结
优点
- 扩展性好:新增策略只需实现接口,符合开闭原则
- 解耦性强:算法逻辑与客户端分离,便于维护
- 支持动态切换:运行时可灵活切换策略,满足不同场景需求
- 符合单一职责:每个策略类只负责一种算法逻辑
缺点
- 类数量增加:每个策略需要一个独立类,策略较多时类数量膨胀
- 客户端需了解策略:客户端需要知道有哪些策略,选择合适的策略
- 策略间可能有重复代码:相似策略可能需要重复实现部分逻辑
使用场景
java.util.Comparator:比较策略接口java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor:拒绝策略接口javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet:doGet/doPost等请求处理策略
策略模式通过将算法封装为独立类,使系统在不修改原有代码的情况下,可以支持算法的扩展和切换。